Describe the Electrodes in This Iron Copper Galvanic Cell
Up to 256 cash back Get the detailed answer. Cateogorize as Zinc or Copper.
Solved Part A Describe The Electrodes In This Zinc Copper Chegg Com
Up to 256 cash back A.

. Drag the appropriate items to their respective bins. B cathode c gains mass d losses mass. Submit A galvanic cell or voltaic cel produces.
A galvanic cell is composed of two half cells ie oxidation half cell and reduction half cell. What is the standard potential Eâ cell for this galvanic cell. Hence anode is Nickel.
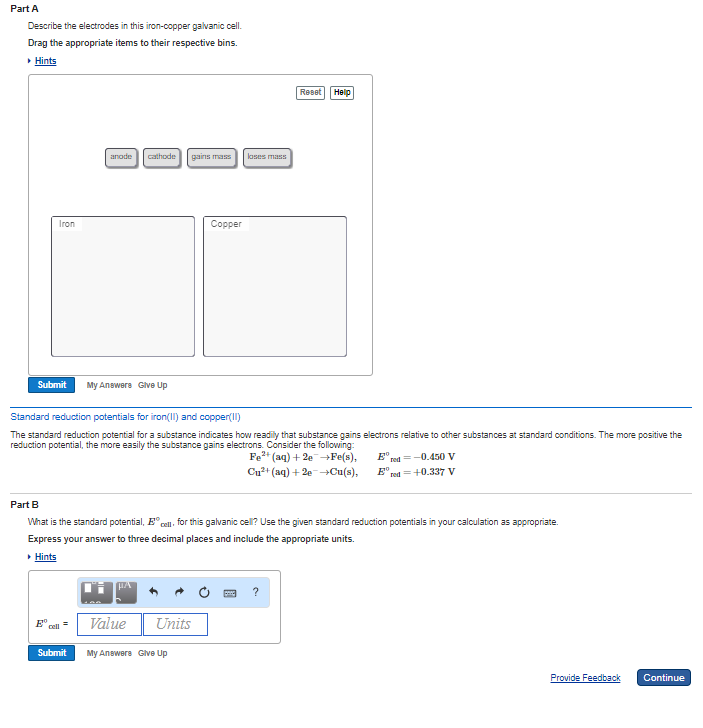
Therefore the copper electrode is the anode. The anode is an electrode wherein the loss of mass takes place in composed of zinc while the cathode wherein it is the electrode that the gain of mass take place is composed of copper. Describe the electrodes in this nickel-copper galvanic cell.
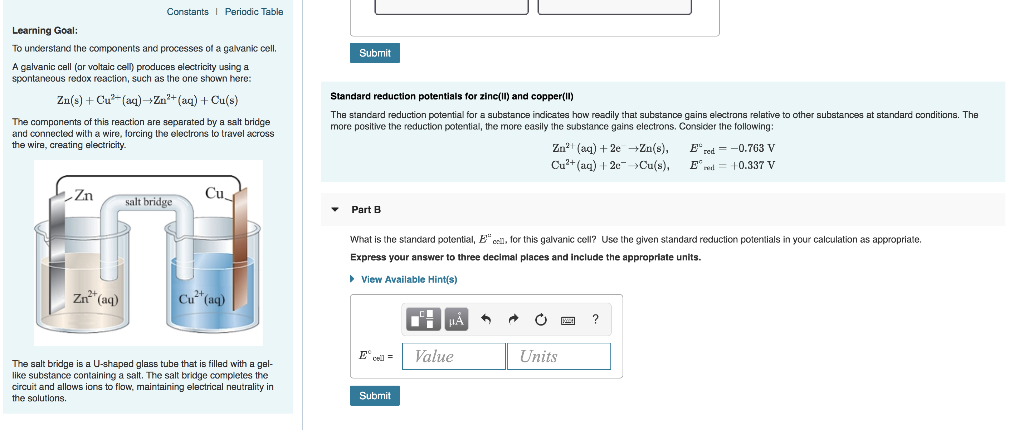
At anode oxidation takes place. This is the simplest type of electrode where metal is dipped into a solution of as ions. Part A Describe the electrodes in this zinc-copper galvanic cell.
View Available Hint s Reset Help anode cathodegains mass loses mass Zinc Copper Constants Periadic Table Learning Goal To understand the components and processes of. In any galvanic cell with reactive electrodes the mass of the cathode increases and the mass of the anode decreases while the cell is operating. By definition a galvanic cell consists of redox processes wherein electrical is.
Use the given standard reduction potentials in your calculation as appropriate. Nickel electrode is dipped in solution. Nickel-Copper cell electrodes are Ni and Cu rod.
The reduction occurs at the reduction electrode ie a cathode and it involves the gain of electrons. Describe the electrodes in this zinc-copper galvanic cell. A galvanic cell consists of two half-cells each containing a metal cathode immersed in a solution of its cations connected via a salt bridge.
Why is a salt bridge necessary in galvanic cells like the one in Figure 2. The copper metal is an electrode. Anode is Nickel and Cathode is copper.
The more positive the reduction potential the more easily the substance gains. The more noble metal copper acts as the cathode and the more active iron acts as an anode. For example a silver rod immersed in a solution of Ag ions or copper rod in a copper sulphate solution.
A galvanic cell is fabricated by connecting two half-cells with a salt bridge one in which a chromium wire is immersed in a 1 M CrCl 3 solution and another in which a copper wire is immersed in 1 M CuCl 2. 2The standard reduction potential for a substance indicates how readily that substance gains electrons relative to other substances at. These electrodes are immersed in copper sulfate in the case of the copper electrode and zinc sulfate in the case of.
GET 20 OFF GRADE YEARLY SUBSCRIPTION. An active metal electrode was found to gain mass as the oxidation-reduction reaction was allowed to proceed. In your case the two half-cells contain a zinc electrode and a copper electrode respectively.
Drag the appropriate items to their respective bins. Drag the appropriate items to their respective bins. And are asked to extract the iron through electrolysis.
Describe the electrodes in this iron-copper galvanic cell. It generally consists of two half cells and a salt bridge. Describe the electrodes in this zinc-copper galvanic cell.
The standard reduction potential for a substance indicates how readily that substance gains electrons relative to their substances. The oxidation occurs at the oxidation electrode ie an anode and it involves the liberation of electrons. Of the reaction is 0567V.
25 represents a galvanic cell. A copper anode in a copper nitrate Cu NO 3 2 aq solution and a silver cathode in a silver nitrate AgNO 3 aq solution. Two half-cells in a galvanic cell consist of one iron Fes electrode in a solution of iron II sulphate FeSO4aq and a silver Ags electrode in a silver nitrate solution.
Activity 531 Writing Galvanic Cell Schematics. The anode is connected to a voltmeter with a wire and the other terminal of the voltmeter is connected to a silver electrode by a wire. Ag s Ag aq e.
Anode Loses mass Copper. For example steel and copper electrodes immersed in an electrolyte Fig. These electrodes consist of a pure metal M in contact with a solution of its cation Mn.
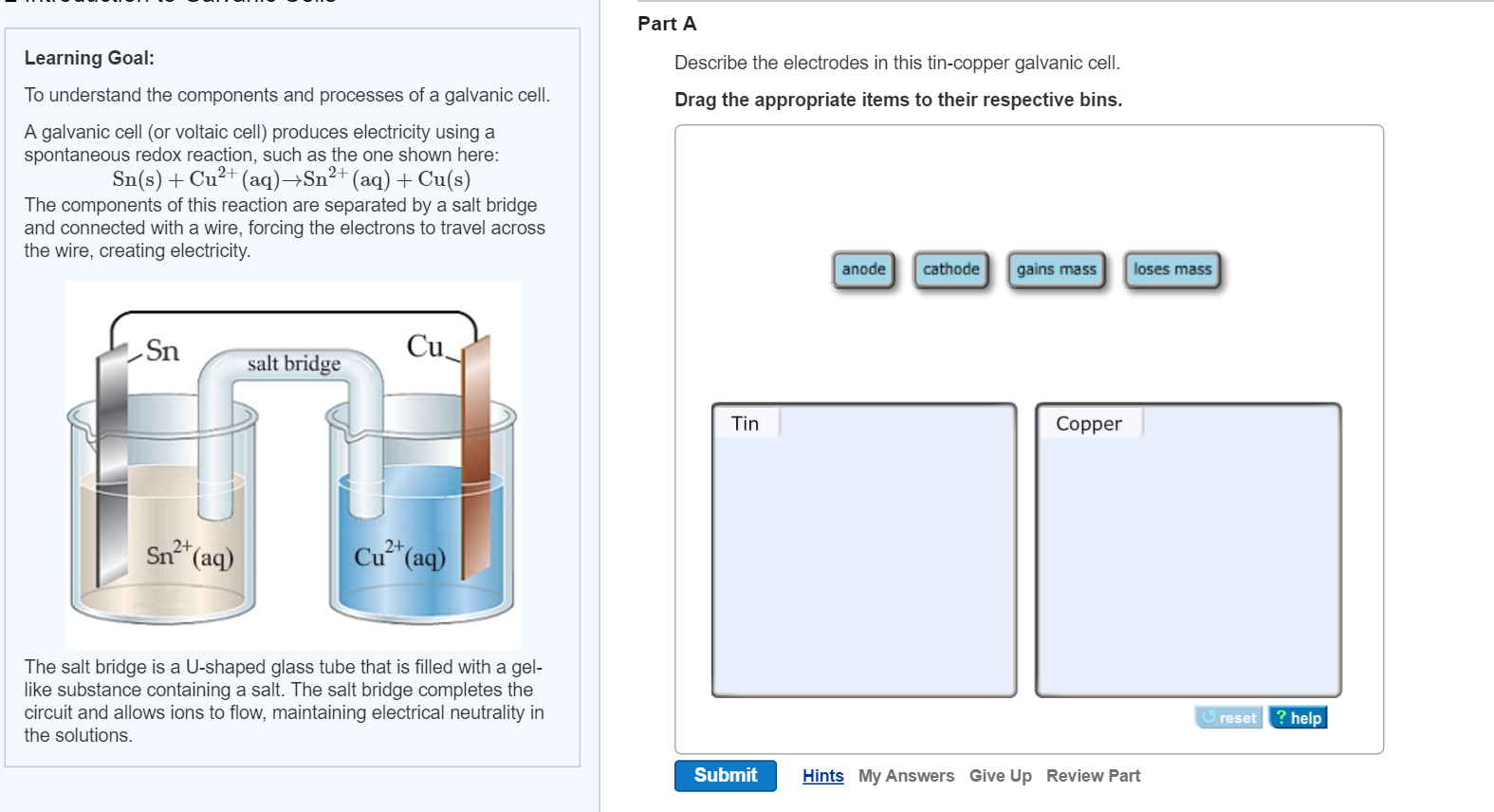
Give equations for the half-reactions that take place at the anode and cathode. Describe the electrodes in this tin-copper galvanic cell. What can be said about the merits of molten versus aqueous FeI2.
Lets first understand how a copper-iron galvanic cell works. A galvanic cell consists of two half-cells. These two half-cells are connected to a voltmeter and a switch externally with the help of metallic wires.
Start studying CHEM 4311 HW7 in progress collab CR DONE. LIMITED TIME OFFER. Describe the electrodes in this zinc-copper galvanic cell.
Describe the electrodes in this iron-copper galvanic cell. Each half cell further consists of a metallic electrode dipped into an electrolyte. The galvanic cell may have an anode or cathode of dissimilar metals in an electrolyte or the same metal in dissimilar conditions in a common electrolyte.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. The standard reduction potential for a substance indicates how readily that substance gains electrons relative to their substances at standard conditions. The copper is undergoing oxidation.
Hence Cathode is copper. In a galvanic cell the two half-reactions combine to 2LisCl2g2Liaq2Claq. Anode cathode gains mass loses mass.
1Describe the electrodes in this zinc-copper galvanic cell. Copper electrode dipped in solution. Therefore the silver electrode is the cathode.
In a copper-iron galvanic cell the copper electrode is the cathode or the positive electrode and the iron electrode is the anode. Assuming the chromium wire functions as an anode write the schematic for this cell. Electric work done by a galvanic cell is mainly due to the Gibbs energy of spontaneous redox reaction in the voltaic cell.
At cathode reduction takes place. One half-cell consists of a silver electrode in a 1 M AgNO 3 solution and in the other half-cell a copper electrode in 1 M CuNO 3 2 is oxidized. The silver is undergoing reduction.
Solved Describe The Electrodes In This Iron Copper Galvanic Chegg Com
Solved Part A Learning Goal To Understand The Components And Chegg Com

No comments for "Describe the Electrodes in This Iron Copper Galvanic Cell"
Post a Comment